Understanding Customer Churn dives into the world of customer behavior, shedding light on why customers leave and how businesses can combat this trend. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of customer churn in a whole new light!
In this guide, we’ll uncover the different types of customer churn, the factors that influence it, methods for measuring it, strategies to reduce it, and the role of predictive analytics in tackling this common business challenge.
Introduction to Customer Churn

Customer churn refers to the rate at which customers stop doing business with a company. It is a crucial metric for businesses as it directly impacts revenue and growth. Understanding customer churn is essential for companies to identify and address issues that may be causing customers to leave.
Common Reasons Why Customers Churn
- Poor customer service: Customers are more likely to churn if they have a negative experience with customer service.
- Price increases: When customers perceive that the value they receive is not worth the price they are paying, they may decide to churn.
- Competitor offerings: If a competitor provides better products or services, customers may choose to switch.
- Lack of engagement: Customers who do not feel connected or engaged with a company are more likely to churn.
- Product issues: If a product does not meet the customer’s expectations or needs, they may look for alternatives.
Types of Customer Churn
When it comes to customer churn, there are different types that can occur depending on various factors. Understanding these types is crucial for businesses to address the issue effectively.
Voluntary vs. Involuntary Churn
- Voluntary Churn: This type of churn occurs when customers actively decide to end their relationship with a company. It could be due to dissatisfaction, better offers from competitors, or changing needs.
- Involuntary Churn: On the other hand, involuntary churn happens when customers are lost without their intention, such as when a credit card expires, a customer passes away, or their circumstances change unexpectedly.
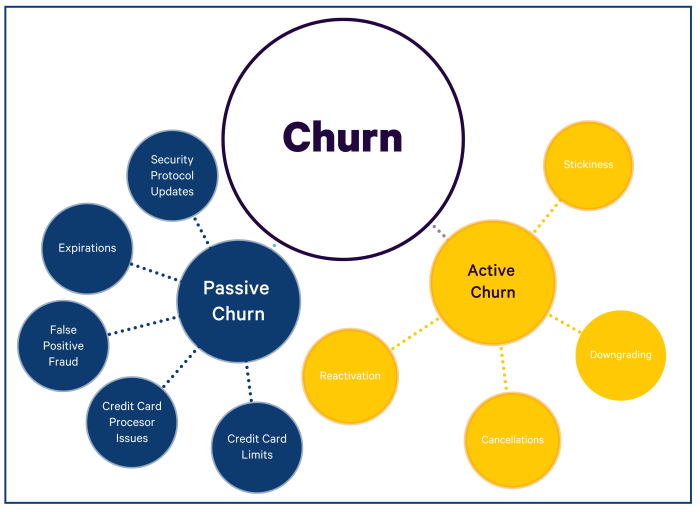
Passive vs. Active Churn
- Passive Churn: Passive churn refers to customers who stop using a product or service without canceling it. They may simply forget about the subscription or not find the value in continuing to use it.
- Active Churn: Active churn, on the other hand, involves customers who actively cancel their subscription or service. They make a conscious decision to leave and take steps to end their relationship with the company.
Examples of each type of customer churn could include a customer voluntarily canceling their subscription to a streaming service (voluntary churn), a customer’s credit card expiring and resulting in a failed payment (involuntary churn), a customer forgetting to use a software tool they are paying for (passive churn), and a customer contacting customer support to cancel their membership (active churn).
Factors Influencing Customer Churn: Understanding Customer Churn
Customer churn is influenced by a variety of factors that can impact a business’s bottom line. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce churn rates and improve customer retention.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction plays a significant role in determining the likelihood of churn. Satisfied customers are more likely to stay loyal to a brand, while dissatisfied customers are at a higher risk of churning. It is essential for businesses to prioritize customer satisfaction through excellent products, services, and support to minimize churn rates.
Pricing
Pricing is another critical factor that can influence customer churn. Customers are sensitive to pricing changes and may choose to switch to competitors if they perceive better value elsewhere. Businesses need to carefully consider their pricing strategies to remain competitive in the market and retain their customer base.
Competition
The level of competition in the market can also impact customer churn. If competitors offer superior products or services at a lower price point, customers may be tempted to switch brands. Businesses must stay informed about their competitors’ offerings and continuously innovate to stay ahead and retain customers.
Customer Service
Customer service plays a crucial role in customer retention. Poor customer service experiences can lead to dissatisfaction and ultimately churn. Businesses need to invest in training their customer service teams to provide excellent support and address customer issues promptly to prevent churn.
Methods for Measuring Customer Churn
Measuring customer churn is crucial for businesses to understand and improve customer retention. There are different metrics used to measure customer churn, each providing valuable insights into customer behavior and satisfaction.
Customer Churn Rate vs. Customer Retention Rate
When it comes to measuring churn, two key metrics are customer churn rate and customer retention rate. Customer churn rate is the percentage of customers who have stopped using a company’s product or service over a specific period. On the other hand, customer retention rate is the percentage of customers that a company has retained over the same period.
Customer churn rate = (Customers at the beginning of the period – Customers at the end of the period) / Customers at the beginning of the period) x 100%
Customer retention rate = 100% – Customer churn rate
Significance of Tracking Customer Churn Over Time
Tracking customer churn over time is essential for businesses to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for improvement. By analyzing customer churn rates over different periods, companies can pinpoint when customers are most likely to churn and take proactive measures to retain them. Additionally, tracking customer churn helps businesses evaluate the effectiveness of their customer retention strategies and make necessary adjustments to enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Strategies to Reduce Customer Churn
Reducing customer churn is crucial for the long-term success of any business. By implementing effective strategies, businesses can retain customers and increase loyalty, ultimately leading to higher revenue and profitability.
Implement Customer Loyalty Programs
One successful strategy to reduce customer churn is to implement customer loyalty programs. These programs incentivize customers to continue doing business with the company by offering rewards, discounts, or exclusive offers for their loyalty.
Provide Exceptional Customer Service
Another important strategy is to provide exceptional customer service. By ensuring that customer concerns are addressed promptly and effectively, businesses can build strong relationships with their customers, increasing the likelihood of retention.
Personalize Customer Experiences, Understanding Customer Churn
Personalizing customer experiences is key to reducing churn. By understanding the unique needs and preferences of each customer, businesses can tailor their products and services to meet those specific requirements, creating a more engaging and satisfying experience for the customer.
Utilize Data Analytics
Utilizing data analytics can also help in reducing customer churn. By analyzing customer behavior and identifying patterns, businesses can proactively address potential issues and offer targeted solutions to improve customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Predictive Analytics and Customer Churn
Predictive analytics plays a crucial role in helping businesses anticipate and mitigate customer churn. By analyzing patterns and behaviors, companies can identify customers at risk of leaving and take proactive measures to retain them.
Utilizing Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are at the forefront of forecasting customer churn. These algorithms can process vast amounts of data to uncover hidden trends and indicators of potential churn. By utilizing algorithms like decision trees, logistic regression, and neural networks, companies can predict churn with high accuracy.
- Decision Trees: These algorithms create a tree-like model of decisions based on customer data, making it easier to identify high-risk customers.
- Logistic Regression: Logistic regression analyzes the relationship between customer characteristics and the likelihood of churn, providing valuable insights for retention strategies.
- Neural Networks: Neural networks mimic the human brain’s decision-making process, allowing businesses to predict churn by recognizing complex patterns in data.
Examples of Companies Using Predictive Analytics
Netflix
Netflix utilizes predictive analytics to recommend personalized content to users, reducing churn by keeping customers engaged with relevant shows and movies.
Amazon
Amazon uses machine learning algorithms to predict customer preferences and behaviors, enabling targeted marketing campaigns that enhance customer retention.
Spotify
Spotify leverages predictive analytics to create customized playlists for users, increasing user satisfaction and reducing churn rates.