Kicking off with Project Management Techniques, get ready to dive into the world of successful project management strategies. From comparing different techniques to exploring real-world examples, this is where the magic happens.
Project Management Techniques
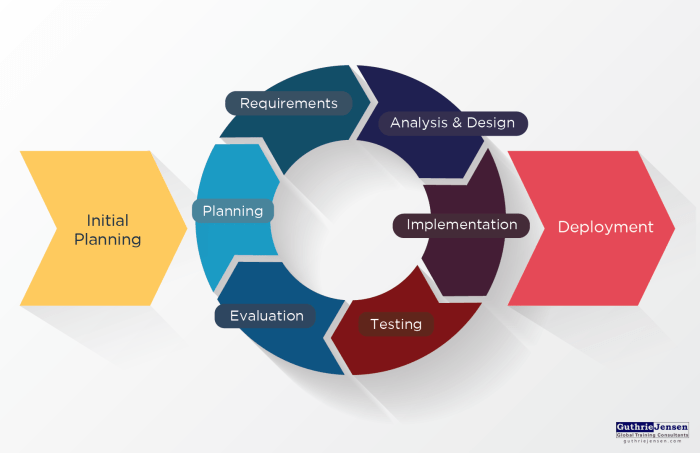
Project management techniques are essential for achieving project goals as they help in planning, organizing, and controlling resources to successfully complete projects within scope, time, and budget constraints. These techniques provide a structured approach to managing projects efficiently and effectively.
Comparison of Project Management Techniques
- Waterfall Methodology: In this traditional approach, each phase of the project is completed before moving on to the next. It is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and little to no changes expected.
- Agile Methodology: Agile is an iterative approach where the project is divided into small increments called sprints, allowing for flexibility and adaptability to changes throughout the project.
- Scrum Framework: Scrum is a subset of Agile that focuses on teamwork, accountability, and iterative progress to deliver high-value products.
- Lean Project Management: Lean focuses on reducing waste and maximizing value, ensuring efficiency in project delivery.
Examples of Successful Projects, Project Management Techniques
- SpaceX Falcon 9 Rocket Launches: SpaceX has successfully utilized Agile methodology to develop and launch Falcon 9 rockets, allowing for rapid iterations and improvements in each launch.
- Toyota Production System: Toyota’s Lean project management techniques have revolutionized the automotive industry by reducing waste and improving efficiency in production processes.
- Apple iPhone Development: Apple’s product development process combines elements of Agile and Scrum methodologies to deliver innovative and high-quality iPhones to the market.
Agile Methodology: Project Management Techniques

Agile methodology is a project management approach that emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and collaboration throughout the project lifecycle. Unlike traditional project management methods that follow a linear and sequential process, Agile promotes iterative development, frequent feedback, and continuous improvement.
Benefits of Agile Methodology
- Increased flexibility to adapt to changing requirements
- Enhanced collaboration among team members
- Higher customer satisfaction due to regular feedback and incremental delivery
- Improved project transparency and visibility
Challenges of Implementing Agile Methodology
- Resistance to change from traditional project management mindset
- Difficulty in estimating time and cost for each iteration
- Dependency on active involvement and availability of team members
- Risk of scope creep without proper monitoring and control
Real-World Examples of Companies Using Agile Methodology
1. Spotify: The music streaming giant uses Agile to continuously deliver new features and updates to its platform, keeping pace with user demands and market trends.
2. Amazon: The e-commerce giant employs Agile to manage various projects simultaneously, ensuring quick responses to changing market conditions and customer needs.
3. Google: The tech giant utilizes Agile to innovate and develop new products rapidly, staying ahead of competitors and meeting user expectations.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
In project management, the Critical Path Method (CPM) is a vital tool used to schedule and manage complex projects. It helps project managers identify the sequence of tasks that are crucial for the successful completion of a project within a specified time frame.
Steps in Creating a CPM Schedule
To create a CPM schedule for a project, the following steps are typically involved:
- Identifying all the tasks and activities required for the project.
- Determining the dependencies between these tasks, i.e., which tasks must be completed before others can start.
- Estimating the duration of each task and the total project duration.
- Creating a network diagram that visualizes the sequence of tasks and their dependencies.
- Calculating the earliest start and finish times, as well as the latest start and finish times for each task.
- Identifying the critical path, which is the longest sequence of tasks that determines the shortest possible project duration.
- Monitoring the progress of tasks on the critical path to ensure timely completion of the project.
Utilizing CPM can help project managers identify the most crucial tasks and ensure timely project completion by focusing on the critical path and managing resources effectively.
Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of project management as it helps in identifying potential threats or uncertainties that could impact the project’s success. By integrating risk management techniques, project managers can proactively address and mitigate risks, ensuring the project stays on track and within budget.
Importance of Integrating Risk Management Techniques
Effective risk management involves a systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks throughout the project lifecycle. It helps in minimizing the impact of unexpected events, ensuring that the project objectives are met within the defined constraints.
- Identification of Risks: The first step in risk management is to identify potential risks that could affect the project. This involves brainstorming sessions, historical data analysis, and expert judgment to create a comprehensive list of risks.
- Assessment of Risks: Once risks are identified, they need to be assessed in terms of their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on the project. This helps in prioritizing risks and focusing on the most critical ones.
- Mitigation of Risks: After assessing risks, mitigation strategies are developed to reduce the probability of risk occurrence or minimize their impact. This could involve risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk mitigation, or risk acceptance.
Examples of Effective Risk Management
Effective risk management has helped prevent project failures or minimize their impact in various industries. For example, in the construction industry, proactive risk management techniques such as conducting thorough site inspections, using quality materials, and implementing safety protocols have helped reduce accidents and project delays. Similarly, in the technology sector, identifying potential cybersecurity risks and implementing robust security measures have prevented data breaches and system failures.