Cross-Selling Techniques: where savvy marketers thrive in the art of boosting sales and captivating customers with strategic upselling tactics. Get ready to dive into a world of innovative strategies that drive business success.
In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of cross-selling, from understanding customer behavior to implementing effective strategies that yield impressive results.
Introduction to Cross-Selling Techniques
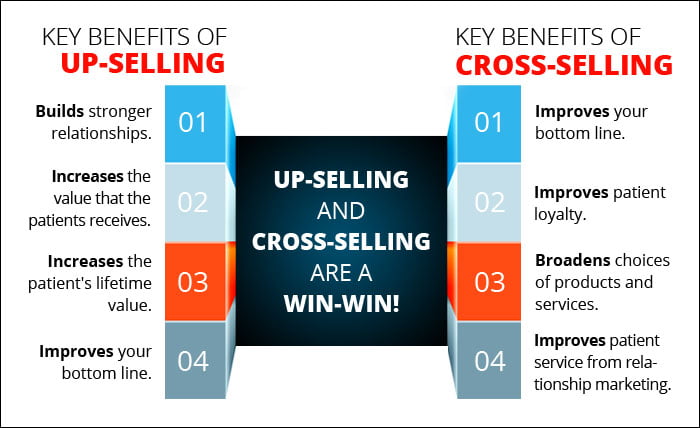
Cross-selling is a sales technique where a company promotes additional products or services to existing customers. It involves offering related or complementary items to what the customer is already purchasing.
Businesses use cross-selling as a way to increase revenue, enhance customer loyalty, and improve overall customer satisfaction. By suggesting additional products that complement the customer’s initial purchase, companies can maximize the value of each transaction and build stronger relationships with their customers.
Examples of Successful Cross-Selling Strategies
- In the retail industry, companies like Amazon use cross-selling by recommending related products to customers based on their browsing and purchasing history. For example, when a customer buys a camera, Amazon may suggest purchasing additional lenses or camera accessories.
- In the banking sector, banks often cross-sell products such as credit cards, insurance, or investment accounts to their existing customers. For example, a customer who opens a savings account may be offered a credit card with special benefits or rewards.
- In the fast-food industry, restaurants like McDonald’s employ cross-selling by suggesting combo meals or upsizing options to customers ordering individual items. This encourages customers to spend more and increases the overall value of their purchase.
Understanding Customer Behavior: Cross-Selling Techniques
Consumer behavior analysis plays a crucial role in identifying cross-selling opportunities. By understanding how customers think, feel, and make purchasing decisions, businesses can tailor their cross-selling strategies to meet their needs and preferences.
Customer segmentation is another key aspect of effective cross-selling. By dividing customers into different groups based on demographics, behavior, or purchasing patterns, businesses can target specific segments with personalized cross-selling offers that are more likely to resonate with them.
Role of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is essential for effective cross-selling because it allows businesses to tailor their offers to specific customer groups. For example, a clothing retailer may target customers who have previously purchased formal wear with cross-selling offers for accessories like ties or belts. By understanding the preferences of each segment, businesses can increase the likelihood of successful cross-selling.
Customer Persona Responses
- High-Spenders: Customers who frequently make large purchases may respond well to cross-selling offers for premium products or services that complement their main purchase.
- Bargain Hunters: Customers who are price-conscious may be more receptive to cross-selling offers for discounted or value-added products that provide cost savings.
- Loyal Customers: Repeat customers who have a strong relationship with a business may appreciate exclusive cross-selling offers or rewards that enhance their overall experience.
- Impulse Buyers: Customers who make quick purchasing decisions may respond positively to cross-selling offers that are presented as limited-time deals or bundles.
Implementing Cross-Selling Strategies
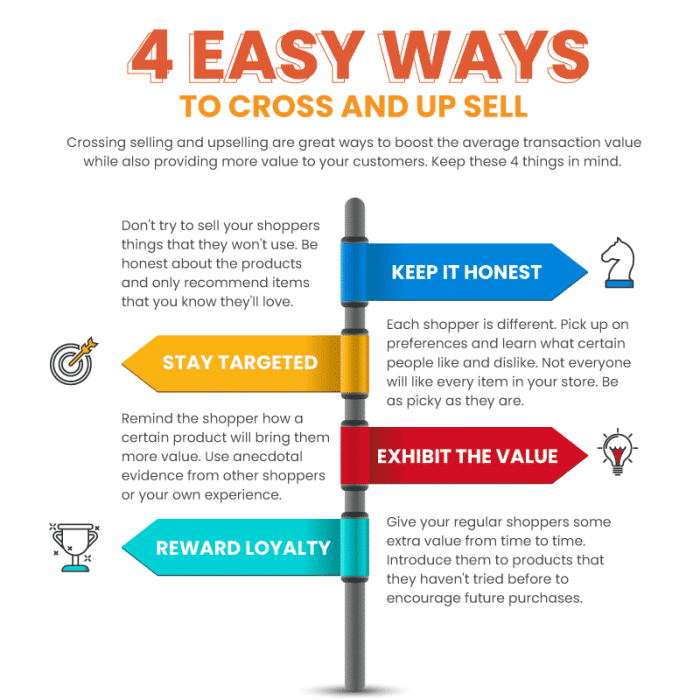
Implementing cross-selling strategies is essential for maximizing sales and increasing customer satisfaction. By utilizing common cross-selling methods such as product bundling and upselling, businesses can effectively boost revenue and enhance the overall customer experience.
Product Bundling
Product bundling involves offering customers a package deal that includes multiple products or services at a discounted price. This strategy encourages customers to purchase more items than they initially intended, increasing the average order value and maximizing revenue. By bundling complementary products together, businesses can provide added value to customers while increasing sales.
- Bundle related products or services that are frequently purchased together.
- Offer a discount or special promotion to incentivize customers to buy the bundled package.
- Highlight the benefits of purchasing the bundle, such as cost savings or convenience.
Upselling
Upselling involves persuading customers to upgrade to a more expensive or premium version of a product or service. By highlighting the additional features or benefits of the higher-priced option, businesses can increase the value of each sale and maximize revenue. Upselling is an effective way to increase customer loyalty and satisfaction by offering personalized recommendations based on their needs and preferences.
- Identify opportunities to upsell during the sales process, such as recommending a higher-tier product or add-on.
- Emphasize the added value or benefits of the more expensive option to justify the higher price.
- Provide personalized recommendations based on the customer’s purchase history or preferences.
Data Analytics and CRM Software, Cross-Selling Techniques
Data analytics and CRM software play a crucial role in optimizing cross-selling efforts by providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns. By analyzing customer data and leveraging CRM software, businesses can create targeted cross-selling strategies that are tailored to individual customers, increasing the likelihood of a successful sale.
- Utilize data analytics to identify cross-selling opportunities based on customer purchase history and behavior.
- Segment customers into groups based on their preferences and buying habits to create personalized cross-selling offers.
- Integrate CRM software into the sales process to track customer interactions and feedback, enabling businesses to provide relevant cross-selling recommendations.
Cross-Selling Best Practices
When it comes to cross-selling, implementing best practices is crucial for maximizing sales opportunities and enhancing customer satisfaction. Let’s dive into some key strategies that can help businesses excel in their cross-selling efforts.
Importance of Personalized Recommendations
Personalized recommendations play a vital role in cross-selling success. By understanding the preferences, needs, and buying behavior of individual customers, businesses can offer tailored product suggestions that are more likely to resonate with them. This personalized approach not only increases the chances of a successful cross-sale but also improves customer loyalty and engagement.
Significance of Timing and Context
Timing and context are essential factors to consider when making cross-selling offers. By presenting relevant product recommendations at the right moment in the customer’s journey, businesses can effectively capture their interest and increase the likelihood of a purchase. Whether it’s suggesting complementary products during checkout or offering upgrades based on previous purchases, timing and context can significantly impact the success of cross-selling initiatives.
Case Studies of Companies Excelling in Cross-Selling
- Amazon: Through its sophisticated recommendation engine, Amazon provides personalized product suggestions to customers based on their browsing history and purchase behavior. This targeted approach has significantly contributed to Amazon’s cross-selling success.
- Starbucks: Starbucks leverages customer data to offer personalized recommendations through its mobile app. By analyzing customer preferences and purchase patterns, Starbucks suggests relevant products and promotions, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
- Netflix: Netflix utilizes data analytics to recommend movies and TV shows to its subscribers, creating a personalized viewing experience. By understanding the viewing habits and preferences of users, Netflix effectively cross-sells additional content, driving engagement and retention.